Dale Rohlfing, D.C., drums up some good news!
July 28th, 2011
.
Hey, … Dale Rohlfing… wasn’t this guy at Fiesta Mexicana Wednesday night???
What’s this all about? Here’s Mickey Hart’s take on it, from his testimony before the Senate:
Rhythm as a tool for healing and health in the aging process
Senate Speech – Mickey Hart
Good morning. Thank you for inviting me to speak to you on an issue of great importance to me. This is the issue of how drumming, the rhythmic manipulation of sound, can be used for healing and health. I also would like to express my support for the concept of preventive, rather than crisis medicine,and specifically the role of music therapy as a means of maintaining mental, spiritual and physical health in people of all ages.
I am a professional percussionist. For over 40 years I have lived and played with rhythm; as an entertainer, as an author, and, always, as a student. Over the last ten years, I have spent much of my time exploring rhythm and it’s affect on the human body. Why is it so powerful and attractive? I have written on this subject in my books Drumming at the Edge of Magic and Planet Drum which try to address these questions. And yet I know that I have barely scratched the surface, particularly regarding the healing properties of rhythm and music.
Everything that exists in time has a rhythm and a pattern. Our bodies are multi-dimensional rhythm machines with everything pulsing in synchrony, from the digesting activity of our intestines to the firing of neurons in the brain. Within the body the main beat is laid down by the cardiovascular system, the heart and the lungs. The heart beats between sixty and eighty times per minute and the lungs fill and empty at about a quarter of that speed, all of which occurs at an unconscious level. As we age, however, these rhythms can fall out of synch. And then, suddenly, there is no more important or crucial issue than regaining that lost rhythm.
What is true for our own bodies is true almost everywhere we look. We are embedded within a rhythmical universe. Everywhere we see rhythm, patterns moving through time. It is there in the cycles of the seasons, in the migration of the birds and animals, in the fruiting and withering of plants, and in the birth, maturation and death of ourselves. Rhythm is at the very center of our lives. By acknowledging this fact and acting on it, our potential for preventing illness and maintaining mental, physical and spiritual well-being is far greater.
As a species, we love to play with rhythm. We deal with it every second of our lives, right to the end. When the rhythms stop, so do we. And this is where music becomes important. According to the late ethnomusicologist John Blacking, music is a mirror that reflects a culture’s deepest social and biological rhythms. It is an externalization of the pulses that remain hidden beneath the busy-ness of daily life. Blacking believed that a large part of music’s power and pleasure comes from it’s ability to reconnect us with the deeper rhythms that we are not conscious of. And it is the connection with these rhythms that gives music the power to heal.
Music as humanly organized sound or vibration has played a pivotal role in the development of our species, beginning with toolmaking. The tool record- all those delicately chipped arrowheads and choppers- is a dramatic illustration of our battle to master the subtle body rhythms that any advanced civilization requires to survive. In order to create the tools that allowed us to move forward as a species, we learned to scrape, strike, rub, shake and swing in rhythm. From there, we gathered in groups to sing our songs, to tell our stories, to dance our dances, all in rhythm. We found that by gathering together in this way, it reinforced our sense of community and family. The natural extension was the use of rhythm, and specifically percussion instruments, in healing ceremonies by traditional medical practitioners.
As modern technology takes us further and further from our natural rhythms, the use of percussion for healing has greater potential than ever. Today, without thoroughly understanding it, thousands of people across the country have turned to drumming as a form of practice like prayer, meditation or the martial arts. It is a practice that is widely acknowledged to help focus attention and to help people break free of the boredom and stress of daily life. More importantly, drumming is a way of approaching and playing with the deeper mysteries of rhythm.
Typically, people gather to drum in drum “circles” with others from the surrounding community. The drum circle offers equality because there is no head or tail. It includes people of all ages. The main objective is to share rhythm and get in tune with each other and themselves. To form a group consciousness. To entrain and resonate. By entrainment, I mean that a new voice, a collective voice, emerges from the group as they drum together.
The drummers each bring their own instruments and drum together for about a half hour. Afterward there is a discussion of issues of importance to the group. The drumming helps to facilitate this discussion because as they drum the group forms a common bond. From groups of women drummers, to twelve step groups like alchoholics anonymous to gatherings of men who are part of the ever-growing men’s movement, drumming is used to open up channels of communication and foster community and family. While some drum groups form around a particular issue, others have no agenda whatsoever, except to allow the members an opportunity to come together, play their instruments and share rhythm.
Older Americans are largely unfamiliar with this movement and yet these are the people who could benefit the most. The formation of drum circles among the elderly should be an integral part of any music therapy program. There is a large and enthusiastic group of drummers who could be called upon to lead workshops and make instructional videos to be distributed among the older population now isolated in nursing homes and retirement communities. It would be emphasized that the object is not public performance. Because, when we speak of this type of drumming, we are speaking of a deeper realm in which there is no better or worse, no modern or primitive, no distinctions at all, but rather an almost organic compulsion to translate the emotional fact of being alive into sound, into rhythm, into something you can dance to. Through drum circles, the aging population could tap into this realm, into these rhythms. The benefits would be wide-ranging.
First, there would be an immediate reduction in feelings of lonliness and alienation through interaction with each other and heightened contact with the outside world. While today many older people spend hours each day sitting in front of the television, drumming is an activity which would allow them direct exposure to younger people from the outside community. Whereas verbal communication can often be difficult among the generations, and in the sickly, in the drum circle non-verbal communication is the means of relating. Natural by-products of this are increased self-esteem and the resulting sense of empowerment, creativity and enhanced ability to focus the mind. Not to mention just plain fun. This leads to a reduction in stress, while involving the body in a non-jarring, safe form of exercise that invigorates, energizes and centers.
There is no question of the substantial benefits which could be derived from increased funding for the study and research of music therapy. This funding is critical to explore the most effective ways to utilize the techniques described here and by the other speakers. Billions of dollars are spent each year for crisis care, while little energy is spent trying to figure out how to avoid the crisis to begin with. A shift from crisis to preventive medicine needs to occur. The introduction of drum circles and percussion instruments into the older American population is a new medicine for a new culture. It was a good idea 10,000 years ago, and it is a good idea today.
Wind projects aren’t benign, to birds, or to humans…
July 25th, 2011
The importance of siting properly — maybe the message is getting through? Just like a nuclear plant, you can’t be putting generators in the ground without a lot of respectful planning and consideration for neighbors, be they the people living next door or the migratory birds making their way through, or in their foraging, roosting and nesting territory.
Eagles are as much an issue here as with the CapX 2020 Brookings transmission line crossing of the Minnesota River, and will be an issue with any of the proposed crossings for the CapX 2020 transmission line across the Mississippi River, which is North America’s major migratory flight path. Eagles in the proximity of transmission lines was the reason (arguably, because the real reason was that they couldn’t use the Myrick Road route, but that’s a whole ‘nother post, see www.nocapx2020.info and search for “Myrick”).
When you’re planning utility infrastructure, and permitting it, you’ve got to have concerns for impacts, but when it’s no
longer the “Environmental Quality Board” handling it, and it’s the Dept. of COMMERCE with their COMMERCE charge, humans and eagles don’t have a chance against the corporate promoters of these projects. It’s time to transfer review back to the Environmental Quality Board and develop standards for siting (do you know there are NO standards for
siting wind projects over 25MW? They just do it on a case by case basis, with no scientific basis whatsoever), and eliminate the Dept. of Commerce and their corporate shills from any oversight of utility projects, unless they want to intervene as a party.
Yesterday there were two articles on this, in the STrib and the LA Times:
Bald eagles could thwart Red Wing wind farm
Wind farms multiply, fueling clashes with nearby residents
Here are the full articles so they’ll be around once archived. First from the STrib:
Bald eagles could thwart Red Wing wind farm
* Article by: JOSEPHINE MARCOTTY , Star Tribune
* Updated: July 25, 2011 – 1:57 AMIn battle against a Red Wing project, citizens turn to a national symbol.
But there is no certainty such a plan will succeed in protecting eagles or other endangered species.
But that’s only if the deaths are discovered.
“If there are 50 birds hit, are they going to tell anyone?” he said. “We hope they would.”
And in the L.A. Times:
Wind farms multiply, fueling clashes with nearby residents
By Tiffany Hsu, Los Angeles Times
Reporting from Tehachapi, Calif.—
Tehachapi activist Terry Warsaw said he’s worried his community will soon be surrounded by turbines.
“They are not benign things,” she said. “We’ve seen turbines go berserk.”
“Monstrous insects,” she calls them. “I look at the propellers for a moment and my head gets dizzy.”
“We are resembling hundreds of towns around the country,” she said.
Some suggest that removing trees to make way for the machines could lead to erosion and flooding.
NPS pressured about Susquehanna-Roseland EIS
July 21st, 2011
First, the bad news – the Commonwealth Court of Pennsylvania has affirmed the Order of the Pennsylvania Public Utilities Commission approving the Susquehanna-Roseland transmission project:
Commonwealth Court of Pennsylvania – Affirms Pennsylvania’s S-R Order
And now, on to the pressure… The National Park Service is working to do it’s job as steward of our national park land, in this case, the federally declared Wild and Scenic Delaware River and the Delaware Water Gap.
Seems that some don’t think they should be allowed to do that job, and are pressuring them to “hurry up” so the Susquehanna-Roseland transmission line can steamroll on through. Well, BACK OFF!
Today the pressure on NPS was overt in two venues. First, U.S. Rep. Charlie Dent (R-PA) amends a bill to push the NPS to complete its environmental review one year ahead of schedule. Say what?!?!?!
Then in my inbox a sour grapes press release from FERC Commissioner Phillip Moeller whining because the newly adopted rule won’t do what he wants, it won’t address “problems” like NPS doing its proper review of transmission projects:
Here’s the Susquehanna-Roseland specific part:
“While I offer substantial praise for today’s final rule, the Commission should have taken a different approach to several important issues. We must recognize that all of the nation’s difficulties in building needed transmission will not be resolved by this rule. Rather, this rule largely addresses planning for long-distance transmission lines, which is only a subset of the critical issues that are inhibiting needed investment.
This rule cannot address issues like the delays caused by other federal agencies in the siting of important projects, as this Commission lacks the legal authority to require other federal agencies to act. For example, see the comments of PJM in this proceeding at p. 17, which state that:
[t]he PJM Board approved the Susquehanna-Roseland 500 kV line in 2007. The Susquehanna-Roseland line was approved by the state regulatory commissions in Pennsylvania and New Jersey for 2012. The line is currently delayed by the National Parks Service [sic] and is not expected to be in service until 2014 at the earliest.
Ohhhhhhhh, isn’t it too bad. He’s just one Commissioner, and he’s got to put his dissent out there as an extensive and extended rulemaking proceeding closes… Why is he pushing, why does he care, and why does his care rise to the level that he sends out a dissenting press release? Lighten up, the National Park Service has a job to do. As the testimony in the Susquehanna-Roseland proceeding before the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities reflects, we are NOT going to freeze in the dark in an incubator without a job…
And here’s Pre. Charlie Dent’s whine:
Charlie Dent pushes expedited federal review of Susquehanna-Roseland power line proposal
Published: Thursday, July 21, 2011, 4:30 AM
By Tom Rowan Jr. | The Express-TimesAnd the New Jersey Sierra Club wants Dent, R-Lehigh Valley, to back off.
If it passes through the House, it would be referred to the Senate.
LIARS – 9,504 MW is NOT record peak demand for Xcel
July 19th, 2011
Read the STrib today? Xcel has 9,500 record peak.
Xcel, how dare you… the 9,500MW peak you report is exaggerated… naughty, naughty. You didn’t deduct for the interruptible service customers’ megawatts, and you’re including electricity you’ve generated and sold elsewhere, that the number represents the totals Xcel put on the grid, and not accounting for the demand that they’ve shed, not wholesale sales in other markets. THIS IS NOT PEAK DEMAND!!! YOU’RE CHEATING, XCEL… sigh… what’s new…
Thanks for clearing that up, little birdie!
But even considering that sleight of hand, it’s no record, it’s not even up to the 2006 peak… and that was FIVE years ago. Your CapX 2020 transmission is predicated on 2.43% (is that right, 2.4 something…) increase annually, but folks, we’re not even close to that.
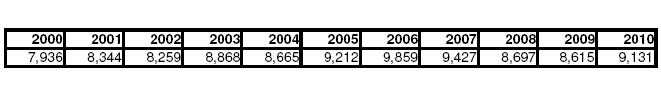
Here’s the peak demand over the last 10 years:
And here’s what the STrib said today, what they said that Xcel said, blah blah blah, 9,500 my ass:
Bent Tree Wind Farm Sound Levels
July 14th, 2011
From Albert Lea Tribune, Fair Use, capturing one of those classic “oh shit…” moments in trucking… (see article below).
In another “oh shit” moment, the Bent Tree Wind Farm noise testing report is out, was released about a month ago, and I’m finally getting around to publishing it.
Bent Tree – Survey of Operational Sound Levels
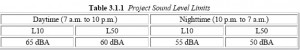
Take a look at p. 19 and 20 for L10 and L50 levels, and look how frequently the levels are higher state noise limits! See Minn. Rule 7030.0040:
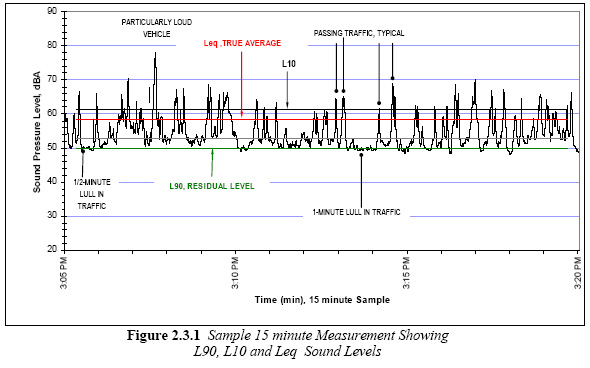
Here’s a summary chart from the Bent Tree noise report, p. 13:
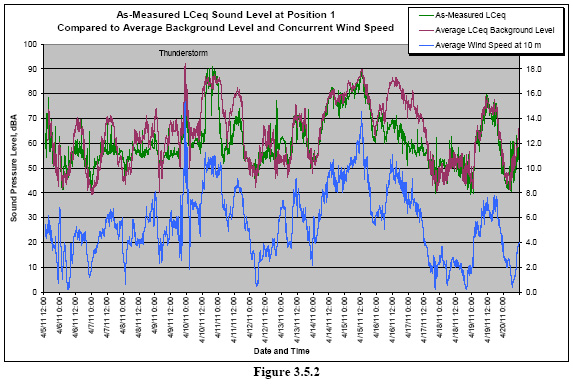
And what they’re trying to do is to remove background sound so that the numbers won’t be above what is allowed by the state’s rules. Graphically, here’s what that comparison, with and without background noise, looks like, p. 43:
The article that was the source of the photo at the top is from the Albert Lea Tribune, and it’s old news, from Sept. 2010, but for those inquiring minds that want to know:
Wind turbine tower falls off truck
Published 9:43am Thursday, September 16, 2010
MANCHESTER — A section of a Vestas wind turbine tower slipped off the semi that was hauling it early Thursday morning.
The truck was carrying the large tower section on gravel 695th Avenue north of Freeborn County Road 29 near West Freeborn Lutheran Church. It fell off near a turn in the road.
The gravel roads in southern Minnesota were saturated after heavy rains Wednesday night. Albert Lea received more than an inch on Wednesday.
Fortunately for the construction workers, the ditch along 695th Avenue was shallow compared to most. It is a minimal traffic road.
Trucks have been delivering these large pieces to each site in the Bent Tree Wind Farm since July.
The Freeborn County Sheriff’s Office responded to the incident. The call went out around 7 a.m. Sheriff Mark Harig said as far as he knew there were no injuries or damages reported.
“It’s just blocking the road,” Harig said.
He said as of 8 a.m. a deputy was still near the site performing traffic control.
“They’ll have to get a crane to pick it up and move it where it needs to go,” Harig said.
Calls to Bent Tree Wind Farm officials were not immediately returned before this story went to press Thursday morning.