Will Delaware, like Illinois, sue FERC and PJM?
July 30th, 2015
Sure hope so — they’ve got it coming. Cost apportionment is a big issue, and for PJM, well, they’d taken their cost apportionment dream to FERC, got the FERC rubber stamp, but it seems they’ve not done a good job of it, according to the Federal Court — that’s old news:
Fast forward to today — turns out Delaware’s Gov. Markell is objecting to costs assessed to Delaware ratepayers, (though I’m not seeing any objection to the project itself coming out of Delaware). DOH! He’d better, this project does nothing for Delaware.
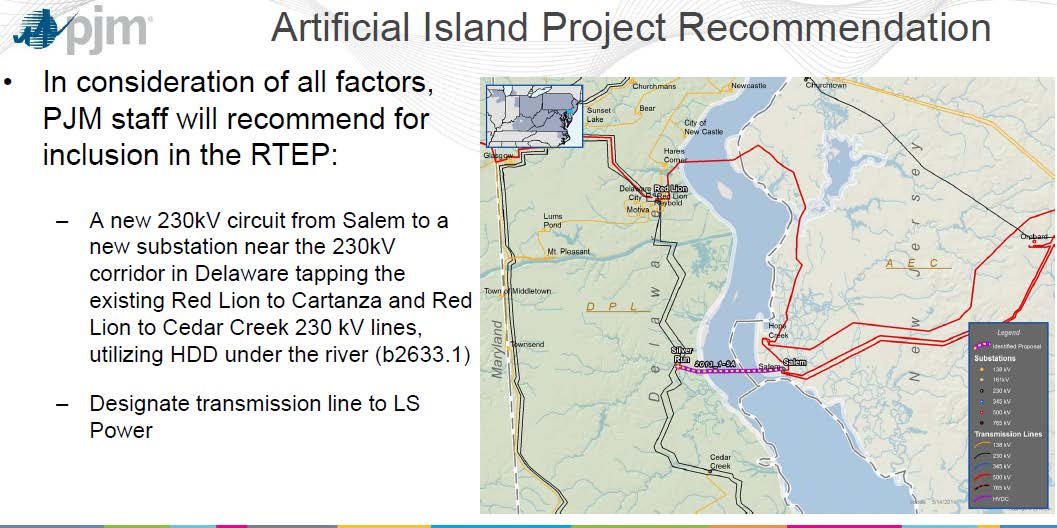
Here’s the PJM Planning doc that tells all:
Note on the first page the statement of need, of why this project is wanted — this is really important:
PJM specified that solution proposals must improve stability margins, reduce Artificial Island MVAR output requirements and address high voltage reliability issues.
So let me get this straight — they’re having stability and reliability issues and PSEG wants to reduce Artificial Island MVAR output requirements, and want to charge Delaware ratepayers for this? PUH-LEEZE… This is a benefit to PSEG, not Delmarva…
And look what our big-coal friends at ODEC have to say:
ODEC letter regarding Artificial Island 7-29-2015
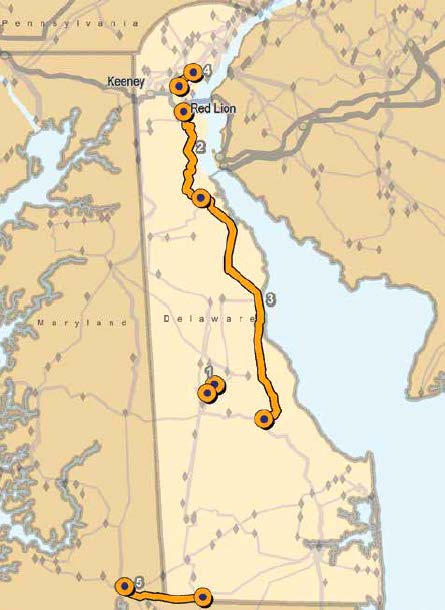
This project taps into the new line that was built not long ago:
Delaware has no regulation of transmission need or siting — so utilities can pretty much do whatever they want. Further, it’s a FERC tariff, so the state doesn’t have anything to say about it going into the rates, and cost apportionment. Great, just great. So now Markell is objecting? It’s a little late…
Delaware needs legislation — legislation like a “Power Plant Siting Act” and a legislative requirement of a need determination for whatever infrastructure they think they want. They need legislation specifying that only Delaware utilities can own and operate transmission in Delaware (see House Bill 387 from the 2014 session). Here’s what House Bill 387 would have done (It would have been an effective good start, protective of Delaware!), establish that a utility wanting to construct and operate transmission demonstrate NEED! Here’s the wording, though it would require quite a bit more, and some solid rules, to be effective:
a.the need for the proposed transmission line;
b.the impact on the reliability of the transmission grid
c.the long term viability of the public utility proposing the line;
d.the technical engineering and operating expertise of the public utility;
e.the technology and design proposed for the new transmission line; and
f.the economic and safety impact of the proposed transmission line.
Here’s the report about this PJM approval from Jeff Montgomery, News Journal:
Disputed cost-shares remain in plan for new power line
Note this snippet:
And here’s the schedule for this project going forward from the PJM Board meeting yesterday:
Seems there’s an opportunity before the FERC ALJ. But before then? What is Delaware going to do? Well, take a look at what Illinois did when it didn’t appreciate the FERC Cost Apportionment scheme — they sued FERC and won, based on the notion that if they weren’t benefitting, they shouldn’t be the ones paying:
The FERC Cost Apportionment scheme was remanded, and it’s in settlement negotiations right now. What is Delaware doing in that docket? To review the public postings, go HERE and search for FERC Docket EL05-121. The next settlement conference is Thursday, August 6, 2015, starting at 10:15 a.m. in a hearing room at FERC HQ. Delaware is represented in this, at least there are Delaware PSC staff listed on the service list, Janis Dillard, John Farber, and Robert Howatt. So what are they doing about this cost apportionment scheme? Seems this settlement conference is just the place for raising a stink about the PJM cost apportionment scheme, to raise issues of “benefits” and “cause cost, pay” arguments. Are they showing up and speaking up for Delaware?
It’s snowing again… another TWO FEET!
February 10th, 2010
My world has turned black and white… here’s the view out the door, the tent for the airplane buckled this morning. We had to go out and get fuel oil for the boiler and gas for the tractor and the roads haven’t been plowed from last weekend’s storm, and here we are now smack dab in the midst of another. The governor has shut down the state, again… and meanwhile, tomorrow at 2 p.m. the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities is making its decision on the Susquehanna-Roseland, delayed from today because of the storm. Well, it’s gonna be storming all day, so I don’t think that this one day will make a difference, other than those of us coming from a distance will probably have a harder time because they’ll be another foot and a half of snow.
Our little tent roof wasn’t the only one collapsing. It could be a lot worse. Schools, big boxes all over Delaware, and even the Townsend Fire Company roofs have collapsed:
Fair Use from The News Journal/ESTEBAN PARRA
Houses too:
And then there’s the Smithsonian warehouse:
… and more view out the window back door — those crab pots aren’t going anywhere anytime soon. Just so that tree doesn’t come down on the van:
Offshore transmission, NOT transmission from Midwest
December 6th, 2009
By standing up for offshore transmission for wind, Delaware’s Gov. Jack Markell stands up to Midwest coal!
The Mid-Atlantic states have been standing up and opposing transmission from the Midwest. They’ve gone on record in a number of venues, and in their opposition are citing Midwest transmission promoters’ disregard for eastern renewable efforts, that xmsn may well not be an economical way to get power to the east, and that THEY KNOW THAT MIDWEST TRANSMISSION PLANS INHERENTLY ARE ABOUT COAL. The plan they’re referring to is a massive transmission buildout known as JCSP, and it also applies to the big PJM buildout that includes the PA-NJ Susquehanna-Roseland transmission line that was the subject of a hearing last month.
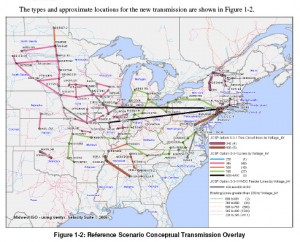
Here’s JCSP (Joint Coordinated System Plan) note their site now talks about wind — but look where the transmission starts, DUH! The coal fields of the Dakotas:
Gotta give them, Delaware, Maryland and Virginia, a lot of credit for recognizing and stating what Midwest states have been unwilling to admit.
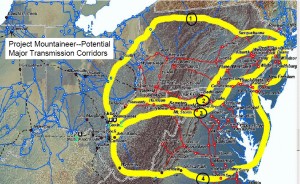
That said, here’s what Mid-Atlantic states are doing — they’re banding together to propose offshore transmission. If it’s underwater offshore transmission, that’s an idea that’s hard not to like. But I’ll bet it throws PJM for a loop, what with all their “backbone” transmission schemes, a la Project Mountaineer, that are in the works:
The FERC birth of Project Mountaineer:
And you can see that those lines in play now, PJM’s “backbone” transmission projects like Susquehanna-Roseland (NE part of Project Mountaineer Line 1) and MAPP (NE part of Project Mountaineer Line 4) are part of the plan… the big transmission plan that does not work for the east coast.
Here’s the Memorandum of Understanding between Delaware, Maryland and Virginia:
And recently, Gov. Jack Markell addressed these issues before American Wind Energy Association’s offshore windfest — but given the PJM big-transmission-projects-from-hell are referred to as “backbone” projects, I wish they’d find another term:
Delaware energy: ‘Backbone’ power line pushed for wind farms
By AARON NATHANS
The News JournalGov. Jack Markell broached the subject this week in his address to the American Wind Energy Association’s offshore wind workshop, the industry event of the year on this side of the Atlantic. Markell signed onto letters the governors sent to members of Congress this summer, and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission last month.
“Let’s have the conversation,” O’Mara said. “It’s extremely worthy of further study.”
“It obviously won’t happen in the absence of federal leadership,” he said.
Fishermen’s Energy President Daniel Cohen said it’s a good idea, but “it’s another moving part.”
The benefits of building lines transmitting wind power from the Midwest are less certain, he said.
“It will be difficult to get progress in this area until there are clear national goals,” he said.
Note that “cost allocation” is raised. Since the 7th Circuit decision tossing out FERC approval of PJM’s transmission cost allocation dream/nightmare, all transmission projects 500kV and over based on that cost allocation scheme are in limbo.
So as noted, who pays, and submarine transmission is EXPENSIVE, is THE big issue now. It’s the big issue for land transmission, it’s the big issue for offshore transmission, and, given the uncertainty since the 7th Circuit decision, maybe some of the sturm and drang could be circumvented if it’s designed at 345kV or below, and uses the “benefactor pays” theory. We shall see…
Eastern Governors stand up against Transmission!!!
May 6th, 2009
Yeaaaaaaaaaaaa! One for the home team!!!!
First it was NYISO and ISO-New England:
Then it was New York’s Deputy Secretary of Energy testifying before Senate Energy Committee:
And now the Governors from the Northeast and Mid-Atlantic states have stood up against the insane Midwest transmission plans — transmission plans like CapX 2020, JCSP/MTEP, Green Power Express, and the unnamed group announced on April 3rd, starting in North Dakota, banding southern Minnesota, and shooting out into Wisconsin.
Here’s their letter:
It’s blurry, so click the letter and read the whole thing. An eye opener for the Midwest, those who don’t recognize that there’s a big world out there and it’s not all about Midwest wind. Folks, you have a marketing problem, your target market says NO! What about NO can’t you understand?