Major pipeline rupture in SD
April 5th, 2016
There’s a big pipeline eruption underground, to the point that it’s bubbling up out of the ground, discovered by a passerby/landowner, near, but not at, a pumping station.
Why do I say big? Well, for a pipeline to spring a leak, and for it to reach the surface, it must be a lot of oil. And it will be a major effort to find the problem, fix it, and clean up the damage. I won’t use the words “spill” or “leak” to describe it, because those sound so pesky and innocent, and will stick to “eruption” or “disgorge” or some such, to convey the impact and damage expected from something like this.
Try finding news articles about this! Try, I dare ya! There’s not more than a handful.
Keystone pipeline shut down after crude leak in South Dakota
Keystone pipeline springs leak in South Dakota
TransCanada shuts down Keystone pipeline after oil spill in South Dakota
TransCanada shuts down Keystone pipeline after oil seeps to surface
This isn’t going to just go away. Cindy Myers has been posting some great photos, maybe those “supplied” to the CBC are hers? I’ve asked for permission to post… waiting for response.
Scoping Mtg. TODAY – Rochester Gas Pipeline
February 29th, 2016
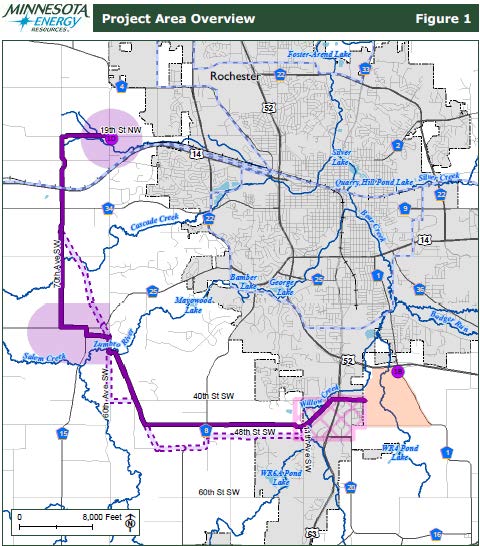
Today it’s a meeting or two about a pipeline, but that’s not all… it’s also about a gas plant at the beginning of this pipeline route!
First the pipeline — Minnesota Energy Resources Corporation is the applicant, and it’s PUC Docket 15-8858, a docket for a pipeline route on the west and southern edges of Rochester, Minnesota, starting at the “Westside” substation on the west side of town, along the big gas transmission pipeline that runs parallel with Hwy. 14. From there it goes a section west, and then south and around to the east.
And lo and behold, last week, Rochester Public Utilities announced its long planned natural gas generating plant for that same location as this pipeline starts, at 19th St. NW and 60th Ave. N. W. This proposed plant was at issue during the CapX 2020 Transmission Certificate of Need docket, where RPU discussed building a natural gas plant in its RPU_34945_Report_June_2005. Here’s the 2015_update_rpu_infrastructure_study. During the CapX 2020 CoN hearing, that notion was pooh-poohed, but we knew better. And voila, here it is!
First they brought it up at RPU Board meetings over the summer:
PUB- Resolution 4315 – Resolution: West Side Energy Station
Westside Energy Station Epc – Bids in Minnesota
And finally, last week, RPU made it’s plans to add new natural gas generation VERY public:
Back in that CapX 2020 Certificate of Need proceeding (PUC Docket 06-1115) it was an issue because the “need” used to justify CapX 2020 transmission to Rochester was so very small that it could be met with this RPU planned natural gas plant. Here’s what I wrote in the 2008 No CapX 2020 Initial Brief:
Most importantly, the need is overstated. In addition to modeling performed with all local generation off line, infrastructure planned was not considered. For example, in Rochester, there are FOUR 161kV lines planned that were not taken into consideration, and which could well serve Rochester’s needs. In addition, RPU, the Rochester utility, has planned for new generation at the West Side substation (Ex. 100, lower left corner), where two of those four lines will be connection to serve Rochester. Ex. 157, Report on the Electric Utility Baseline Strategy for 2005-2030 Electric Infrastructure, June 2005, Summary p. S-21-S-22. Specifically, this report recommends actions that have been taken by RPU, resulting in the Westside Substation and transmission from it to serve the city:
Consider taking options on approximately 100 acres of land within the RPU service territory near a high pressure gas line and transmission facilities under RPU control for installation of future combustion turbine capacity.
…Around 2014, assuming that new generation is required in accordance with the long range plan and that generation has not been installed in connection with the transmission issue, begin the process for installation of approximately 50-100MW of natural gas-fired generation for an inservice date of 2018. The generation should be low capital cost with as low an operating cost as is consistent with expected operating capacity factors.
Id.
Local load as a reason for CapX is not supported by the evidence. The need, even if assumed, can be met in other ways, and these small amounts, if assumed in its entirety, cannot justify a project of this size.
And here we are, deja vu all over again. Guess we need to make sure that phased and connected actions are considered in this pipeline environmental review.
And another thing, this pipeline environmental review — the PUC, despite that Sandpiper case, ordered a “comparative environmental analysis.”
Nope, that “environmental review lite” is NOT sufficient…
Menahga Xmsn Project public hearing TOMORROW!
October 18th, 2015
Yes, it’s TOMORROW! Great River Energy and Minnesota Power want to build a transmission line to solve a distribution problem (age and overloads) and power up pipeline pumping stations for the MinnCan MPL Line 4 and for another “potential” project, oh, maybe, perhaps, the Sandpiper pipeline?
6:00 p.m.
Monday, October 19, 2015
Menahga Senior Center
19 Cedar Avenue
Menahga, MN 56464
For more information, check this Legalectric post:
A transmission project with a pipeline driver
You can see everything in the Public Utilities Commission docket, just go to DOCUMENT SEARCH HERE and search for either Certificate of Need docket 14-787 or Route Permit docket 14-797.
TOMORROW!
Sandpiper-NDPC’s Whale-Eye Inducing Petition
September 21st, 2015
WHAT!?!?! Yes… Really… after the delightful decision from the Appellate Court requiring an Environmental Impact Statement, telling the Public Utilities Commission that an EIS must be completed before a Certificate of Need can be issue, the Applicants dropped Petition. Read this whale-eye inducing filing from North Dakota Pipeline Company, LLC (a/k/a Enbridge) hot off the press:
North Dakota Pipeline Company _ Petition for Rejoinder and Comment Period 20159-114150-03
Here’s the short version:
Once more with feeling, here’s the Appellate Court’s decision:
And the bottom line:
So from this order of the Appellate Court “to complete an EIS” the Applicant now asks for the “need” docket and “routing” docket to be brought back together and to use the “Comparative Environmental Analysis” that the Appellate Court says isn’t sufficient. Yes, that what they’re saying:
What planet is North Dakota Pipeline Company living on? Earth to Mars!!!!! A “CEA” is not sufficient. MEPA requires an EIS. The court told the Public Utilities Commission to complete an EIS. The Court did NOT say to go ahead with a “CEA.”
Not too long ago, Lisa Agrimonti sent around notice that she had moved over to Fredrickson & Byron. $50 says that she’ll be filing Notice of Appearance for this docket!
At long last, EIS is required for Certificate of Need
September 14th, 2015
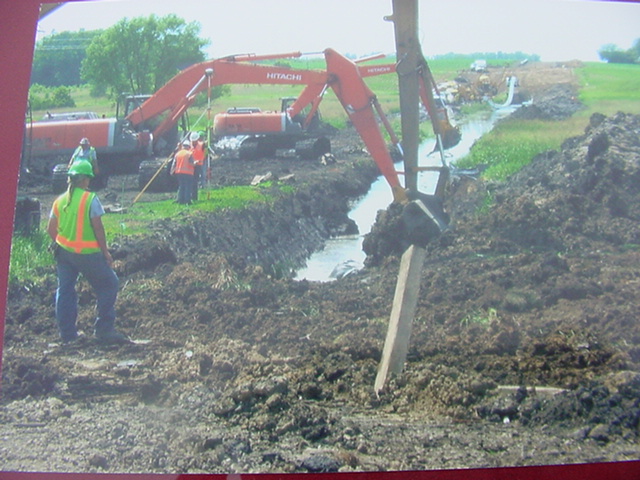 Putting MinnCan pipeline through the Nietes field
Putting MinnCan pipeline through the Nietes field
Today the Minnesota Court of Appeals finally determined that under the Minnesota Environmental Policy Act, a full Environmental Impact Statement, not the abbreviated “Environmental Report,” is required. I’ve been before the Appellate Court, the Public Utilities Commission, the Administrative Law Judge, in Comments to the Dept. of Commerce, and at the Rulemaking Advisory Committee for Minn. R. ch. 7849 how many times on this?!?!? … sigh… OK, whatever…
Sent this to the PUC’s rulemaking staff because we’ve got to make sure the Certificate of Need rules are in line with this decision:
So back to today’s Appellate decision — I’m glad they’re finally acknowledging this problem. Very, very glad to see this order to remand to the Public Utilities Commission for a full Environmental Impact Statement, as required by the Minnesota Environmental Policy Act.
Here is the decision:
Here’s the meat of it — it’s so simple — why did it take so long?





