JCSP Big Picture – who pays? WE DO!
July 2nd, 2013
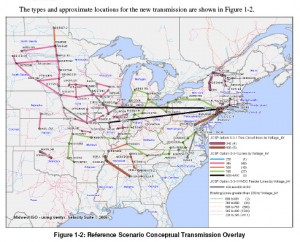
Transmission — it’s all connected. In looking at the Minnesota rulemaking, and the existing and proposed rules that utilize the word “regional,” I’m thinking about big picture stuff, the big proposals in the wings, and that Joint Coordinated System Plan (JCSP) map sure presents a big picture. For some reason, I’ve not been able to find the full JCSP report until recently:
Who cares about JCSP? Well, WE’D better care, because look who’s paying for the transmission build-out (p. 68 of Vol. 1):
Look at the numbers for Midwest ISO, a $-10,293, or for MAPP, a $12,292, that’s a COST, not a savings. MISO and MAPP get nominal production cost savings and massive load COSTS. This is not news, but is worth repeating as we discuss “regional.” And another take with the same take-away of big costs for MISO and MAPP customers, used by our good friends at AWEA to promote this transmission buildout in their flyer called “Green Power Transmission and Consumer Savings” (flyer below):
Read the whole thing:
What a deal, eh?
Look what AWEA has been advocating to make this happen:
DUH… eastern states don’t want our transmission
March 5th, 2010
Repeat after me… EASTERN STATES DON’T WANT OUR MIDWEST TRANSMISSION.
Once more with feeling… EASTERN STATES DON’T WANT OUR MIDWEST TRANSMISSION!!!
And they don’t give a rodent’s rump what we do with our transmission but THEY DO NOT WANT TO PAY FOR IT!
It’s not anything new, but it seems that the message is getting through all the way to Iowa. Soon Minnesota? The message? That the east coast does not want Midwest transmission, that they have their own renewables and not only that, they know that transmission from the Midwest means coal and, most importantly, THEY WILL NOT PAY FOR TRANSMISSION FOISTED UPON THEM.
The 7th Circuit case tossing out PJM’s cost apportionment scheme must be having an impact because everyone is freakin’ about cost allocation. Again, GOOD! The court said that PJM could not shove the costs of transmission on those who do not benefit from it:
Enter the Coalition for Fair Transmission Policy, just launched today with a press conference in Washington, D.C.
Dig this from their site:
HA! I love it when that happens…
Here’s some background on our Midwest Transmission — transmission we don’t need and they don’t want:
This opposition to Midwest transmission is nothing new, I’ve entered documentation in the record in a couple of proceedings now, but what is new is that as of today’s “launch,” there’s now an industry group advocating against Midwest transmission, and that’s one utility interest I’m glad to see hopping mad as hell and not going to take it anymore! GOOD! Maybe that will help stop this stupid transmission-fest across the Midwest.
PUC Chair David Boyd had it right when he testified before Minnesota’s Legislative Energy Commission and led off with, “We need a business plan.” Yes, that’s true, there is no business plan, and there is no MARKET for transmission. I just hope that message gets through before “we” build and WE have to pay for all these wires in the air!
Here are a few recent posts of mine on this, followed by today’s article in the Des Moines Register.
And today’s Des Moines Register article:
By DAN PILLER • dpiller@dmreg.com • March 5, 2010
Alliant Energy has its objections
But as wind energy becomes bigger and more corporate, the utility industry is divided even in Iowa.
Other states have their own plans
While Iowa has speckled its countryside with wind turbines, other states have similar aspirations.
Atlantic seaboard states advanced plans for offshore wind farms, which they say would eliminate the need to ship wind-generated electricity from Iowa.
Read the rest of this entry »
The Economist weighs in, now it’s YOUR turn!
May 4th, 2009
I’d wondered why “The Economist” had shown up in my blog stats, and now I know. But from the viewpoint of this article, it’s clear they didn’t do more than scratch the surface of transmission in the Midwest. This is “party line” all the way — I hope they’ll now take the time to read NYISO and ISO-NE’s letter of withdrawal from publication of JCSP!
YOUR TURN! Let them know what you think and why — the registration is instantaneous and easy, so COMMENT AWAY!
Spreading green electricity: A gust of progress
Apr 30th 2009 | CHICAGO
From The Economist print edition
Transmission for coal – FERC AD05-3
March 21st, 2009
Yes, all this transmission we see, the hard to believe plans of superhighways across the country, MTEP, JCSP, Green Power Express, TrAIL line, Mid-Atlantic Power Pathway, Susquehanna-Roseland, on and on and on, it’s for coal, we know that, but when the truth jumps up and is as in-your-face as it is at this meeting… well, ya gotta read it to believe it. From the FERC docket entitled PROMOTING REGIONAL TRANSMISSION PLANNING AND EXPANSION TO FACILITATE FUEL DIVERSITY INCLUDING EXPANDED USES OF COAL-FIRED RESOURCES (really, that’s the name…):
Here, from p. 61, is a tantalizing snippet from the Pres. of PJM:
PJM is certainly proud of what has been accomplished to date to open up markets to coal, but there is much more that we and others in this region can do to further enhance that use of coal.
It is for this reason that, today, PJM is setting out by example, a new initiative which we have labeled Project Mountaineer — appropriately titled for the state that we’re in — to utilize our regional transmission expansion planning process to explore ways to further develop an efficient transmission super highway, if you will, to deliver the low-cost coal resources in this region of the country, to market.
And to actually build it when people don’t want it over their land, don’t want to look at it, don’t want the EMF impacts? Well, they say…
About the only answer to that would be some sort of federal siting law that would basically overcome local property rights.
National Interest Electric Transmission Corridors anyone? This was in 2005… as the CapX Technical Report was about to be published, putting all of this into action… sigh….
To look up the entire docket, go HERE and search for AD05-3, and voila, there it is for your edification and reading enjoyment!
It’s all for coal, we know that, and we’ve got to NOT let them get away with this!
JCSP & UMTDI in the news
February 16th, 2009
More transmission – again in the Wall Street Journal.
Hard to tell which of the alphabet soups this article is about, and I’d say both, it’s about the Joint Coordinated System Plan and the Upper Midwest Transmission Development Initiative — UMDTI! But we know it’s all one and the same.
The article doesn’t really specifically name either “group” and it leaves us wondering just who or what is behind it. This is a good thing — yes, it really is as amorphous as it sounds! What disturbs me, of course, is the “It’s for wind,” because we know better!
At least the WSJ noticed the NYISO and ISO-NE’s objections — here it is again, it’s one of those letters I just can’t get enough of:
The UMDTI is insidious, a cheerleading effort to push transmission through. The way the thing is structured, is, as I said in my comments at the February 11, 2009, meeting, is ABSOLUTELY ASS-BACKWARDS. It’s market driven backwards engineering a transmission solution to support nonexistent need.
Upper Midwest Transmission Development Initiative – HOME PAGE
UMTDI Stakeholder Letter 10-28-08
Stakeholder Responses – LINK – look who the stakeholders are – DUH!
Wind on the Wires Comments … sigh…
UMDTI Stakeholder Letter 12-31-08 (Ed Garvey – MISO)
Dec 30 Draft – Cost Allocation Work Group (Marya White – Commerce)
December 30 Draft – Transmission Planning Work Group (Randy Pilo – PSC-WI)
Wind on the Wires cites many studies:
MISO’s Regional Generation Outlet Study (RGOS)
Transmission planning initiatives by” CapX 2020, ATC, Mid-American and others”
Minnesota RES transmission study
MISO’s MTEP-08 and MTEP-09
Joint Coordinated System Planning Stuey
Eastern Wind Integration Transmission Study
None of these studies are linked — and they’re not on the UMTDI site — let’s see how long it takes to find them.
Now for the more difficult ones… one moment please…